Traditional IRA Essentials Tax Rules Roth Comparison
Summary
- Traditional IRAs have eligibility requirements and contribution limits based on factors such as income, filing status, and access to a workplace retirement plan.
- Contributions to traditional IRAs may be tax-deductible, but withdrawals in retirement are subject to ordinary income tax rates and require minimum distributions starting at age 72.
- Roth IRAs do not offer a tax deduction for contributions, but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free and there are no required minimum distributions.
- Consider your income, tax rate, and retirement goals to determine which IRA option is best for you, and consult with a financial advisor for personalized advice.
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on Traditional IRA Essentials Tax Rules and a Comparison with Roth IRAs. In this article, we will explore the fundamental tax rules associated with Traditional IRAs and shed light on how they differ from Roth IRAs. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting your retirement planning journey, this article will provide you with essential insights to make informed decisions about your financial future. So, let's dive in!

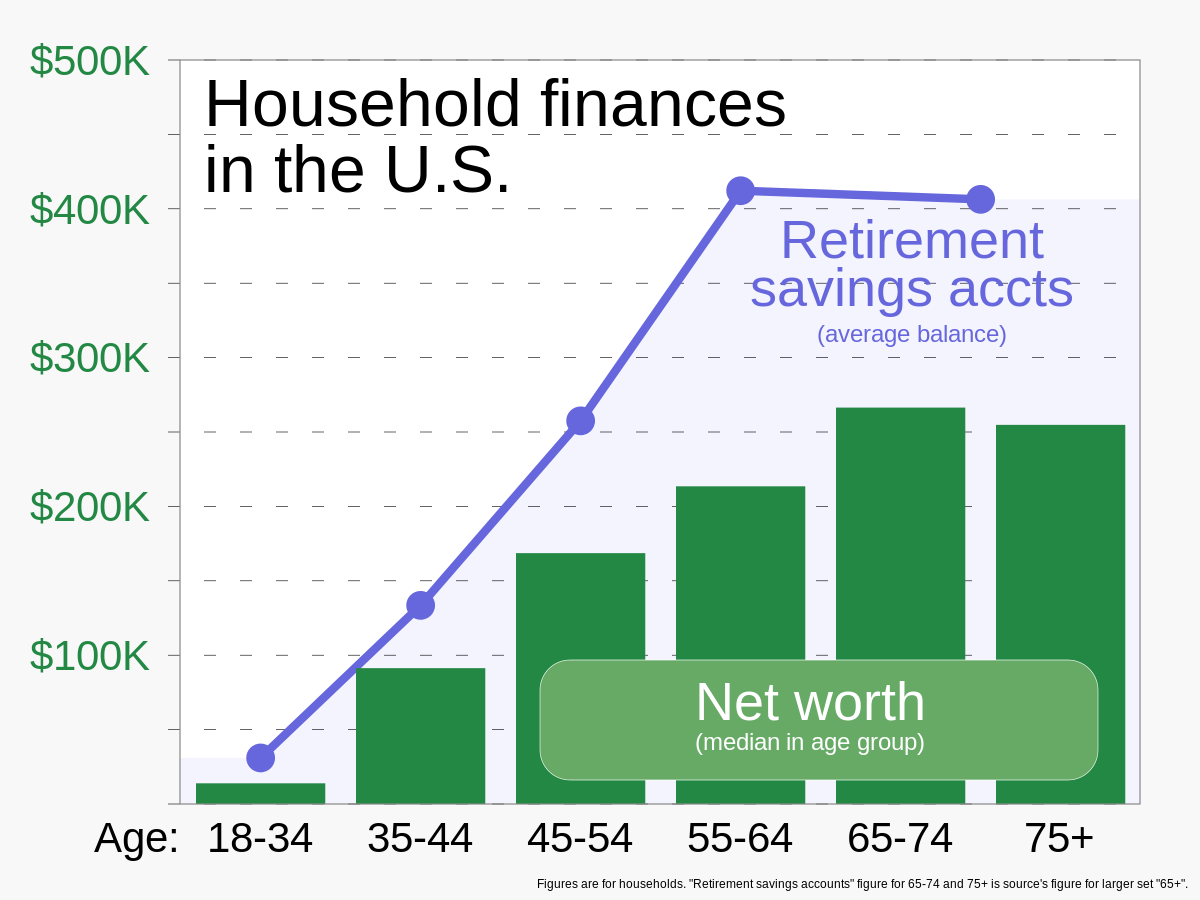
Understanding Eligibility and Contribution Limits
When it comes to traditional IRAs, it's important to understand the eligibility requirements and contribution limits. Eligibility is based on factors such as income, filing status, and whether you or your spouse have access to a workplace retirement plan. Contribution limits are set by the Internal Revenue Service and can change from year to year.
Contributions to a traditional IRA may be tax-deductible, depending on your income and whether you or your spouse have a workplace retirement plan. It's also worth noting that traditional IRAs have required minimum distributions, which are withdrawals that must be taken starting at age 72 to avoid penalties.
Comparing traditional IRAs to Roth IRAs can help you determine which option is best for your retirement savings. Roth IRAs don't offer a tax deduction for contributions, but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
Understanding the tax rules and limits for both traditional and Roth IRAs is essential for maximizing your retirement savings and minimizing your tax liability. Consider consulting with a financial adviser or using a robo-advisor to help you make informed investment decisions within the tax advantages of these retirement accounts.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Contributing
Contributing to a Traditional IRA offers several benefits. Contributions are tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income and potentially lowering your tax bill. Additionally, earnings within the account grow tax-deferred, allowing your investments to compound over time. However, one drawback is that withdrawals are subject to ordinary income tax rates, which could be higher than the capital gains tax rate. Another drawback is the required minimum distribution (RMD) at age 72, which can limit your control over when and how you access your funds.
In comparison, Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement, as contributions are made with after-tax dollars. They also do not have RMDs, providing more flexibility. However, the drawback is that contributions are not tax-deductible, so you don't receive an immediate tax benefit.
Consider your income, tax rate, and retirement goals to determine which IRA is best for you. Consulting a financial adviser or using a robo-advisor can help you make an informed decision.

Comparing Employer Plans and Other IRA Options
| Plan Type | Traditional IRA | Roth IRA | 401(k) | 403(b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Treatment | Tax-deferred | Tax-free qualified withdrawals | Tax-deferred | Tax-deferred |
| Contribution Limits (2021) | $6,000 ($7,000 if age 50 or older) | $6,000 ($7,000 if age 50 or older) | $19,500 ($26,000 if age 50 or older) | $19,500 ($26,000 if age 50 or older) |
| Employer Matching Contributions | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Income Limits for Contributions (2021) | None | Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) phase-out limits apply | None | None |
| Withdrawal Rules | Taxable at ordinary income tax rates | Tax-free qualified withdrawals, contributions can be withdrawn penalty-free | Taxable at ordinary income tax rates | Taxable at ordinary income tax rates |
Guidelines for Distributions and Early Withdrawals
When it comes to your Traditional IRA, it's important to understand the rules and guidelines surrounding distributions and early withdrawals. Early withdrawals from your Traditional IRA may be subject to penalties and taxes, so it's crucial to be aware of the potential consequences. Distributions, on the other hand, refer to the money you withdraw from your Traditional IRA after reaching a certain age. These distributions are typically subject to income tax.
To avoid penalties for early withdrawals, it's important to wait until you reach age 59 ½ to withdraw funds from your Traditional IRA. However, there are certain exceptions, such as using the funds for a first-time home purchase or for qualified education expenses, which may allow you to avoid penalties. Keep in mind that even if you meet the exceptions, you may still have to pay income tax on the distributed amount.
It's important to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to fully understand the guidelines and potential consequences of distributions and early withdrawals from your Traditional IRA. They can provide guidance on the best course of action based on your specific financial situation.
Gold IRA: Should You Open One To Save For Retirement?


