Consider a 401k Plan to Invest Your Retirement
- A 401k plan, or qualified retirement plan, is an employer sponsored plan that allows employees to make pre-tax contributions to their retirement savings.
- This can reduce your billable income, or the amount that your employer withholds from your paycheck for federal income taxes, social security, Medicare, and state income taxes.
- This can reduce your billable income, or the amount that your employer withholds from your paycheck for federal income taxes, social security, Medicare, and state income taxes. 401k plans are funded with pre-tax dollars, which means the money is taken out of your paycheck before taxes are calculated. 401k plans are also funded with pretax dollars, which means the money is taken out of your paycheck before taxes are calculated, and you pay taxes on the money when you withdraw it in retirement.
A 401k plan, or qualified retirement plan, is an employer sponsored plan that allows employees to make pre-tax contributions to their retirement savings. This can reduce your billable income, or the amount that your employer withholds from your paycheck for federal income taxes, social security, Medicare, and state income taxes.

Employers, Individuals and Typical 401(k) Plan Investment Options
A 401(k) plan consists of an employee's contributions, the employer's contributions, and the investments available under the plan.
In general, an employer may match an employee's contribution up to a certain percentage of annual income. For example, an employer may only contribute up to 3% of the employee's annual income.
If an employer matches 100% of an employee's contribution up to 6% of their annual income, it may potentially be advantageous for the employee to contribute 6% of their annual income to a 401(k) plan.
For employees who want to make more money in retirement, it may be advantageous to contribute more than the maximum amount. Since an employer is allowed to match contributions up to a certain percentage of the employee's income, an employee may want to contribute an additional percentage point to increase the amount the employer is willing to contribute.
The maximum contribution limit is currently $19,000 per year. However, employees age 50 and over can contribute an additional $6,000 per year.
A 401(k) plan may include various investment options, including mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and money market funds.
401(k) Plan Fees
The other option for saving for retirement is through a 401(k) plan. These plans are similar to 403(b) plans but are usually offered by larger companies.
401(k) plans often come with fees. You may have to pay a 401(k) administration fee, which varies by plan. Some plans charge a 401(k) fee, which is an annual charge assessed to participants.
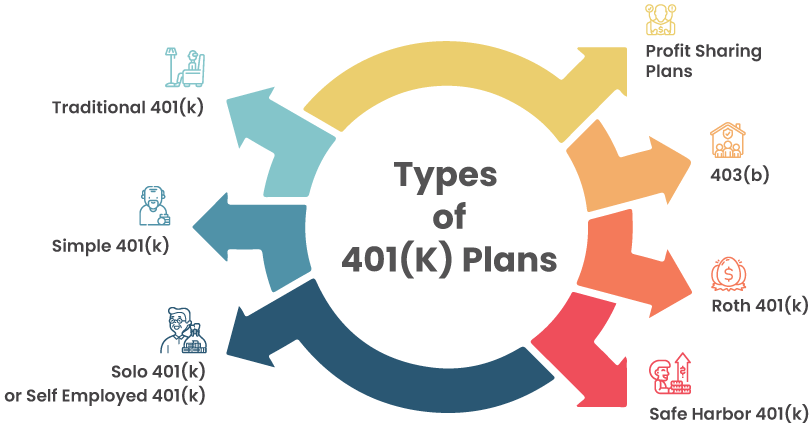
401(k) Plan Types
As an employee, you have a number of retirement plan options that vary based on your company's willingness to sponsor a retirement plan, as well as your willingness to contribute.
Here is a breakdown of some of the most common plans.
Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plan
This type of plan is offered by employers to their workers. Employers may contribute up to 25% of their worker's salaries, or up to $54,000 in 2020.
However, if an employee contributes more than $19,000 annually, he or she is given an extra tax break.
Self-Employed Retirement Plan
This type of plan allows you to contribute up to 25% of your adjusted gross income (AGI) or up to $54,000 in 2020.
For 2020, you can put a maximum of $56,000 into a 401(k), 403(b), or 457 plan.
Mutual Funds
While many people view mutual funds as expensive investments, many are unaware that mutual funds are a great deal.
Mutual funds are professionally managed and, depending on the fund, come with low management fees. For example, the average mutual fund charges an annual fee between 0.25% and 1.00%.

401(k) Matching
A 401(k) plan can be an excellent option because it offers tax-deferred accumulation and tax-free growth. Most 401(k) plans offer an employer match. Here's how it works:
When you contribute to a 401(k) plan, your employer matches a portion of your contribution. This is usually a percentage of your salary, often 5%, 7%, or 10%. For example, if you contribute 5% of your salary to your 401(k) plan, your employer will also contribute 5% of your income to the plan.
401(k) Investing Options
A 401(k) plan is a retirement plan that is designed to benefit both the employer and the employee. The employer, usually through payroll deductions, contributes a percentage of each employee's salary to the account. The employee, in turn, contributes a percentage or the entire amount as a pretax contribution.
The account works much like a mutual fund. The contribution, along with any earnings, grows tax deferred. When money is withdrawn from the account, it is taxed as ordinary income.
401(k) Employer Contributions
If your employer offers a 401(k) plan, it may be your only option to save for retirement. A 401(k) plan allows employees to save and invest for retirement on a pre-tax basis. The employer also contributes money on your behalf. In most cases, employees can defer their taxes, up to a certain limit, by saving part of their salary in a 401(k) account.
The gross contribution limit for 2018 is $18,500. The limit for 2019 and 2020 have been reduced due to the pandemic.

